 |
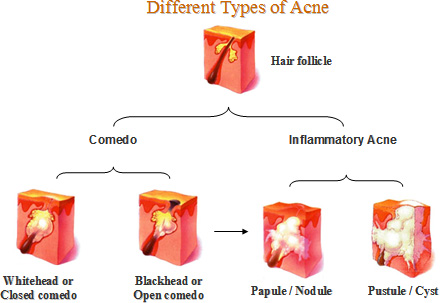
Acne Acne is an upsetting skin condition that commonly affects teenagers but can also affect adults. Disfiguring scars may appear if acne is untreated, therefore early acne treatment is advisable. Acne can be categorized by different types of bumps on the skin, ranging from clogged pores (blackheads and whiteheads), pimples (red bumps or pustules) and deeper lumps (nodules or cysts) that may become painful. These often occur on the face, neck, chest, back, shoulders and even the upper arms. Related Treatment(s): AHA (Glycolic Acid) Rejuvenation Biopsy / Skin Surgery Dermal Fillers – Hyaluronic Acid Gel Fractional Lasers Fractionated Microneedle RF Laser Facial Treatment Microdermabrasion Treatment of acne depends on the severity of acne and its impact on your daily activities. A wide range of topical and oral medications, chemical peels and microdermabrasion can help control, reduce and prevent acne, minimizing potential scarring. Large acne nodules and cysts may be treated by injecting steroids into the bump. For severe cases of acne and acne that is unresponsive to other treatments, an oral medication containing isotretinoin may be used. Certain acne scars may be treated by a combination of surgical treatments,such as subcision and punch excision, fractional laser resurfacing, and the injection of dermal fillers. The results of treatment, however, are variable and could be associated with various side effects. What causes acne?Acne is caused by clogged pores. These pores are medically known as sebaceous follicles. They are in essence sebaceous (oil) glands connected to a hair-containing canal. These sebaceous follicles are found mainly on the face and upper chest and back regions. The sebaceous glands secrete sebum (oil), and are most influenced by male hormones (androgens). During adolescence, androgen levels in both females and males rise, stimulating the sebaceous gland to produce more sebum. In addition, during puberty skin follicle cells are shed more rapidly, and mixed with excess sebum, the opening of the follicle becomes plugged or clogged, creating what we commonly refer to as blackheads and whiteheads (comedones). Normal skin bacteria, known as Propionibacterium acnes multiplies rapidly within the plugged follicle, releasing irritating substances which in turn cause an inflammation and rupture of the follicle walls, resulting in redness, swelling and pus – the pimple. Deeper and more severe inflammation are responsible for nodules and cysts, which have a greater risk of permanent scarring. Skin care adviceFor daily care of your skin, you should wash your face twice a day with a mild cleanser and warm water. Acne is not caused by dirt, therefore frequent or rigorous scrubbing will not help. A moisturizer should be used when the skin is dry, even if you feel you have oily skin. However, choose a moisturizer that is oil-free and “non-comedogenic” (which should not cause whiteheads or blackheads). Remember not to squeeze, pick, scratch or pop your pimples. When pimples are squeezed, as a result there may be more redness, swelling, inflammation and subsequent scarring. If you use cosmetics, look for products that are “non-comedogenic” (do not clog pores) and remember to remove your makeup each night with a mild cleanser and water. It is advised that you avoid sunbeds and prolonged sun exposure in order to prevent damaging your skin or getting skin cancer. Choose a sunscreen that is oil-free, such as a gel or light lotion. |
|
DISCLAIMER: The information contained in this site is strictly intended only for the use of registered patients and is confidential and may be privileged and/or otherwise protected from disclosure. Any unauthorised use, copying, dissemination or any other action taken or otherwise omitted to be taken in reliance upon this information is prohibited.


